The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has been nothing short of revolutionary, continuously reshaping industries and altering our daily lives. As we delve deeper into this technological frontier, staying abreast of emerging trends becomes increasingly challenging. I have been dedicating time to understanding traditional and generative AI, only to discover that the landscape is shifting once again towards a new paradigm: Agentic AI.

In this and subsequent blogs, I am planning to put my learnings and reflections in a series of blogs as I continue my journey of discovery. In this first blog we will take up the journey of evolution of AI starting from traditional to the now in demand, Agentic AI.
Traditional AI: Foundation of AI
Traditional AI, also referred to as weak or narrow AI, has been extensively utilized over time. It operates on pre-defined algorithms and remains integral in data analysis applications. A notable application includes financial forecasting and the identification of fraudulent transactions that deviate from established financial norms.
The primary challenge associated with traditional AI is not merely its domain specificity but rather the availability and labeling of data required to formulate rules. Developing accurate predictive models necessitates an extensive dataset comprising labeled examples.
Let’s take a simple use case. We want to detect if an insurance claim is fraudulent. As a first step, you will need to gather is a huge dataset having transactions marked as fraudulent. Assuming you are a big insurance corporation, you probably have the data. Next task would be do data cleansing/ sanitization and label it so we can have some algorithm built on top of it. When all things are done, we can use some sort of algorithm (an example would be k-means clustering) to figure out what bucket a new data goes in to. The corresponding model that is generated will be able to detect fraudulent insurance claims only. If you want to detect red flags in financial transactions, this will give incorrect results.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning was an evolution in this field bringing in the era of autonomous forms of intelligence. It allowed developers to create models without programming. ML can easily extract patterns out of huge datasets giving it more autonomous form of intelligence. ML as well as Deep Learning paved way for the next generation of Artificial Intelligence.
There are different methods of training the machine learning models.
Supervised Learning
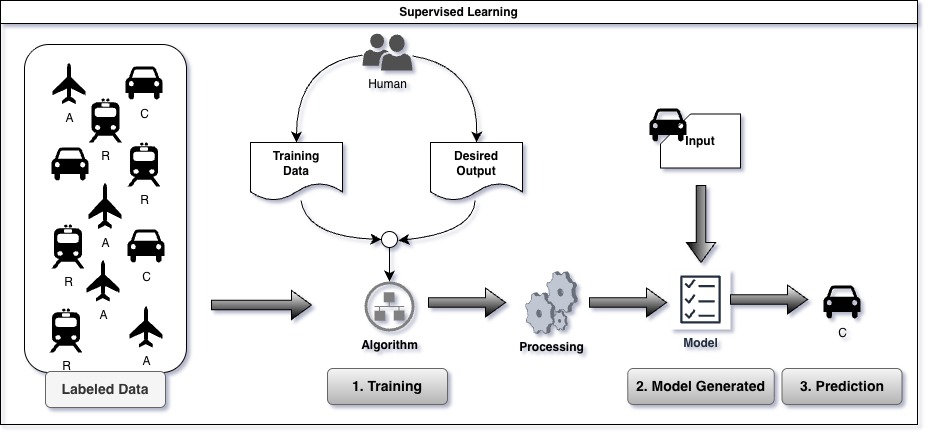
Supervised learning is a machine learning approach where an algorithm learns from labeled training data, consisting of input-output pairs. The model makes predictions on new data by applying the patterns learned during training. It’s widely used in applications like image recognition and spam filtering, excelling at tasks where historical data guides future decision-making.
Supervised learning may be used for spam detection in emails using support vector machines, or it can predict housing prices and fluctuations based on linear regression models. One of the most used application is image classification.
Unsupervised Learning
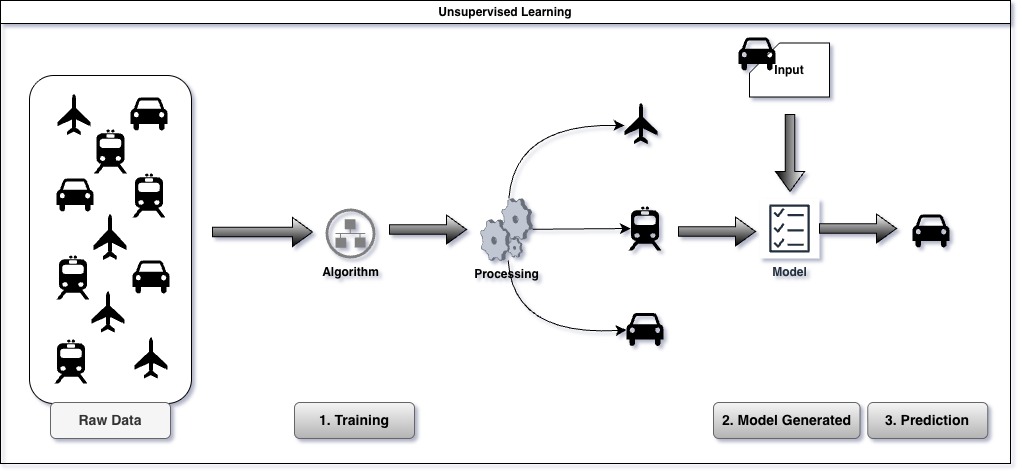
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where algorithms learn patterns from unlabeled data. Unlike supervised learning, it doesn’t rely on predefined labels or outcomes. Instead, it identifies structures and relationships, clustering similar data points and reducing dimensionality to uncover hidden insights. Common techniques include clustering, association, and anomaly detection, making it ideal for exploratory data analysis.
A good use case for unsupervised learning is customer segmentation based on K-means clustering algorithm. Customers can be segregated based on purchasing behavior without any defined categories. Also in cyber security, it can be used for anomaly detection.
Semi Supervised Learning
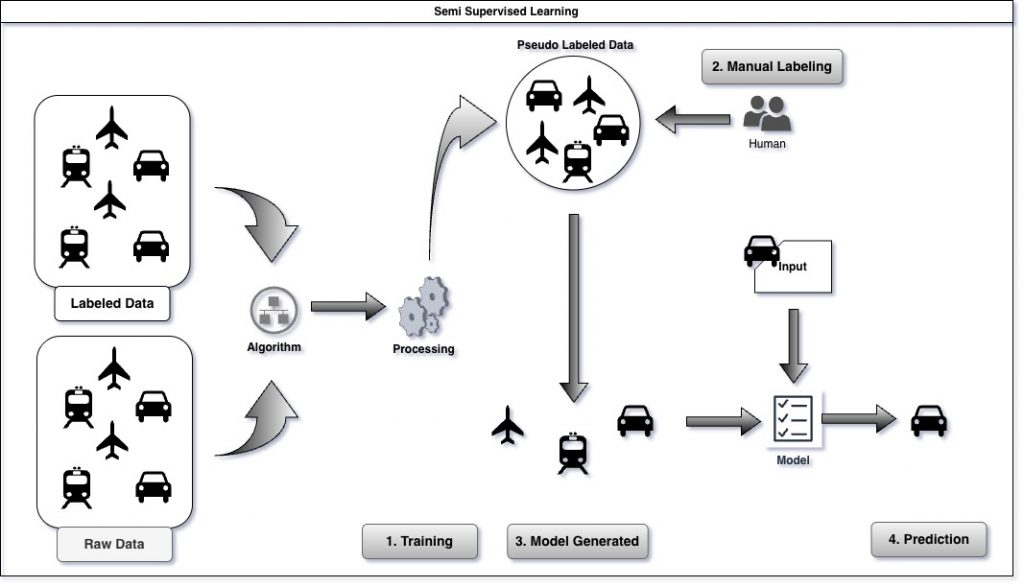
Semi-supervised learning is an approach in machine learning that leverages both labeled and unlabeled data to improve model accuracy. It’s particularly useful when acquiring labeled data is costly or time-consuming, allowing models to learn from the structure inherent in large volumes of unlabeled data, thereby enhancing performance with minimal supervision. This method effectively bridges the gap between supervised and unsupervised learning.
This is used when the number of items in labelled dataset is small. This can be used to enhance speech recognition raw data or small subset of labelled images.
Reinforcement Learning
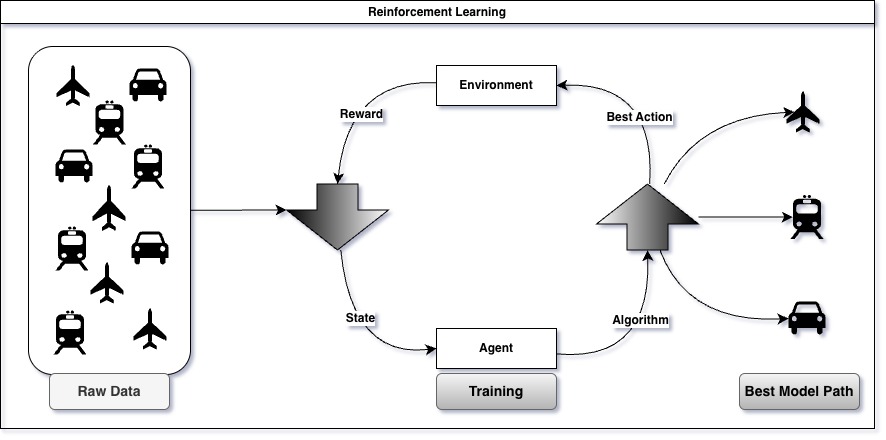
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is an AI approach where agents learn to make decisions by interacting with their environment. Through trial and error, they receive rewards or penalties based on their actions, optimizing behavior over time to maximize cumulative reward. This technique excels in complex, dynamic scenarios like gaming, robotics, and autonomous systems.
One of the most interesting use cases for reinforcement learning is in robotics to train robots. Apart from that it can be used to play a lot of games without specifically coding the rules. Autonomous vehicles also can used reinforcement learning along with supervised learning for obstacle avoidances.
Generative AI
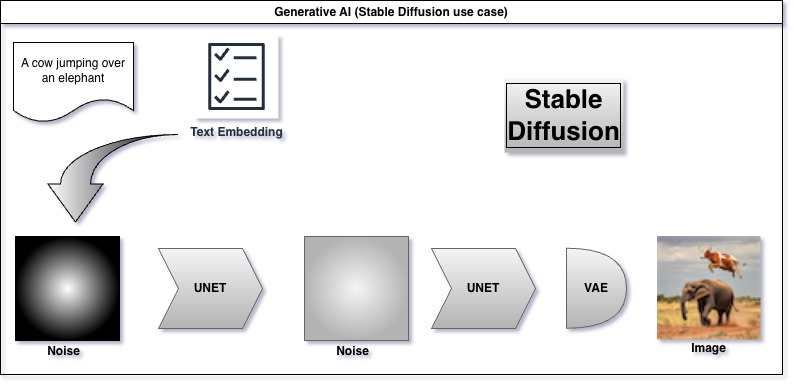
As the name suggests, Generative AI creates content. This ranges from text, images, music and more. Leveraging machine learning techniques, such as neural networks, these systems can produce original outputs by understanding patterns in vast datasets. This technology can work along with other machine language techniques generating new contents.
One of the good use cases that comes to mind is news article generation. Given the correct input, for example scores and key moment from a sports event, these models can generate a nice article for the sporting column.
Agentic AI

Agentic AI represents a significant leap forward by integrating decision-making capabilities into artificial systems, enabling them to act autonomously with specific goals in mind. Previous generation models were all reactive, which means that it would do what it was asked to do. On the other hand, Agentic AI is proactive. It can anonymously make decisions and act on it. The key difference for Agentic AI is that it can understand context and make decisions in real time based on the context. They can “think” or “reason”, which means that they can analyze context and arrive at the context.
Before we talk more about Agentic AI, we have to understand about LLM (Large Language Model) and SLM (Small Language Model).
Agents
AI Agents are autonomous systems that can perform tasks and make decisions without human intervention. They are modeled based on advanced algorithm and training given on large datasets. Any model trained on huge amount of data are known as LLM or Large Language Models.
Agents share the following characteristic,
- Autonomy – they can act independently without human input.
- Reasoning – Continuously analyze data and adjust decisions accordingly.
- Memory – Remember past interactions and can answer follow up questions.
AI agents may also be classified under frontier models (that are trained on huge datasets and have knowledge based on billions of parameters) and open source models (may have smaller number of parameters). Larger the model, more processing power it will need – but will also produce better result.
Agents in Agentic AI
Agentic AI can use multiple agents having different specializations, along with external tools like web search and other input data to make appropriate decisions and complete it without human intervention.
Let’s take an example. When a new employee joins, let’s assume an Agentic workflow takes over the next steps. It can do pre-boarding for employee like creating an employee ID, creating email and messaging handles, ordering all new equipments needed by employee, sending a welcome email along with all first day formality, schedule a virtual training etc. For this it can leverage multiple agents, external tools like email, SAP integration and access to employee records. This entire process can be done autonomously and triggered as soon as an employee is hired.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey towards Agentic AI represents a significant milestone in technological innovation. This evolution marks a transition from simple automation to systems capable of reasoning and making autonomous decisions. As we’ve explored the innovations leading up to this point, it’s clear that Generative AI has played a pivotal role by enabling machines to create, adapt, and learn from vast datasets.
Agentic AI opens new horizons for industries across the board, promising enhanced efficiency in task automation while simultaneously tackling complex decision-making processes. However, with these advancements come responsibilities: ensuring ethical standards, maintaining transparency, and safeguarding against biases are paramount as we integrate more intelligent systems into our daily lives.
As we stand at the threshold of this exciting era, the promise of Agentic AI offers both opportunities and challenges that will shape the trajectory of our digital age.
1 thought on “Navigating the Evolution of AI: Traditional to Agentic AI”